Hello, this is BlackGreenCo:)
Let's find out Lumbar herniated intervertebral disc.
1. What is a Lumbar herniated intervertebral disc?
Our spine is connected by dozens of bones. It is called intervertral disc, or disc, that absorbs the body's impact and acts as a buffer between these vertebrae and bones.

The intervertral disc consists of an inner 80% moisture jelly-like nucleus pulpous and an outer annulus fibrous to protect it. This interstate disc relieves shock and protects vertebrae.
However, as aging progresses with age, nucleus pulpous becomes less hydrated, less elastic, and less shock absorption. As a result, the annulus fibrous becomes weak and partially cracked, resulting in excessive load.
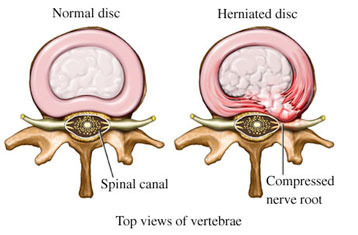
The hardened nucleus pulpous out the weakened aunlus fibrosu, and when it gets worse, some of the nuclei slip out through the nucleus pulpous, causing various neurological anomalies. This phenomenon is known as lumbar herniated intertebral disc, or 'back disc'.
HIVD (Hernified Inter-Vertral Disc)
=HNP (Hernified Nuculus Pulpous)
= HLD (Hernified Lumbar Disc)

In this state, excessive pressure on intervertebral disc may result in secondary degenerative bone spur (=bone growth) and increased load on the facet joint, resulting in other spinal diseases such as Facet Joint Syndrome and Spinal stenosis.
Disc symptoms are known as degenerative diseases caused by aging, which are often known as degenerative diseases caused by aging, resulting in a large number of waist discs as muscles, ligaments and bones around the spine become weaker as you age.
Recently, however, disc symptoms often occur in young people in their 20s and 30s due to their lifestyle, such as sitting in a chair in a bent position for a long time or using a smartphone for a long time in an incorrect position.
2. What are the symptoms of Lumbar herniated intervertebral disc?
- Back Pain.
- Symptoms of numbness in the back, buttocks and legs.
- Backache when cough or sneezing.
- Lying down or comfortable position relieves pain.
- The feeling of heavy pressure and paralysis of the lower body.
- The phenomenon of thinning legs and losing strength.
The main symptoms of Lumbar herniated intervertebral disc are back pain and referred pain. There are many cases of widespread pain around the back to the tailbone, and it can become more painful when moving or changing posture.
In some cases, pain may occur in certain areas, from the waist to the feet, but there may also be pain radiating to the tip of the toes below the knee, and other radiated pain appears in the lesion area.
In particular, the lower limb radial pain, which appears by escaping the disc and stimulating the nerve root directly, is unbearably painful. In severe cases, symptoms such as urinary disorders or lower limb paralysis may occur.
- Progress of lumbar herniated intervertebral disc symptoms

Initial symptom
- In many cases, there is only back pain.
- When sitting, back pain becomes worse and standing helps.
- In the morning, your back and legs feel stiff, but you feel relax the pain when you're active.
- Flexion your back will worsen the pain.
- It's hard to straighten your back when you sit and stand up for a long time.
Worsening symptom
- Waist pain causes scoliosis (functional) with crooked spine.
- Referred pain appears towards the lower extremities with back pain.
- Referred pain in the leg may be more painful than back pain.
- Pain gets worse when you poop, cough, or sneeze.
- Lying down and raising your legs will cause pain.
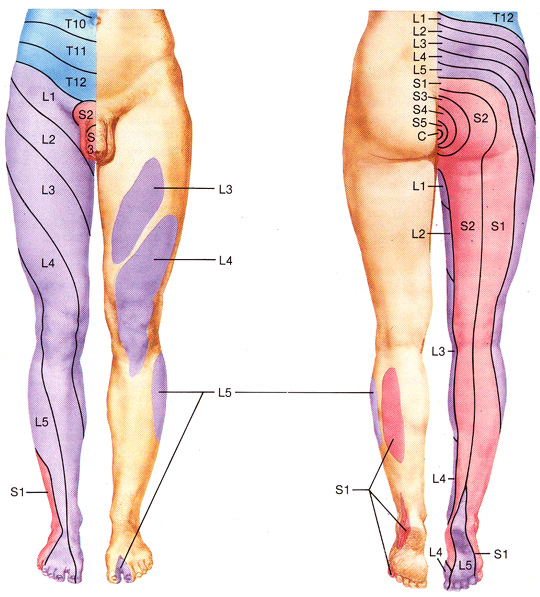
- Referred pain depending on lesion area
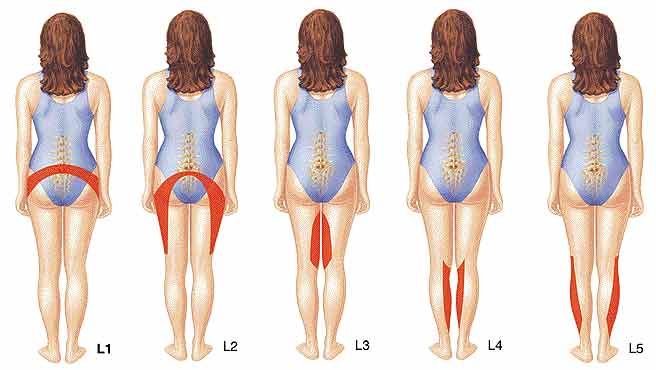
L1~L2: Back to pelvis pain
L2~L3: Back to thigh pain
L3~L4: Pain from hip to inside of the knee
L4~L5: numbness from hip to toe and pain
L5~S1: Feeling numb and pulling from the hip to the heel through the back of the knee popliteal.
3. What is the cause of the lumbar herniated intervertebral disc?
- Sitting in a chair for a long time in a bad position.
- The habit of sitting obliquely on a chair or cross-legged.
- If the back is burdened when lifting heavy objects
- Standing with the back bent and bent or standing in the same position for a long time.
- The habit of lying on one's side or sleeping on one's stomach.
- Reduced bone density and degeneration of disc due to aging
- External impact of traffic accidents, falls, etc.
The main cause of back disc is poor posture, lifestyle, aging, etc. If the vertebrae are twisted and subjected to constant pressure for a long time, the disc between the vertebrae and the bones will be crushed out and pushed.
If the disc is pushed out heavily and continuously stimulated, the annulus fibrous may swell and tear, or the annulus fibrous inside may tear and burst, pushing nucleus pulpous outwards.
In that case, the immune cells in our body can recognize and attack the ruptured nucleus pulpous as a foreign substance, and the various substances that occur in the process can cause pain.
4. What are some good lifestyle habits of lumbar herniated intervertebral disc?
- When sitting on a chair, sit straight with your hips on the backrest.
- When standing, apply force to the abdomen, straighten your back, straighten your chest and pull your chin to stand upright. Stretch whenever you need to stand for a long time.
- When driving, it is recommended that you sit back and bend your knees 60 degrees.
- When lying down, knees slightly bent with the cushion. When you lie down and stand up, turn your body to the side, bend your knees, touch the floor with one hand, and sit slowly.
- If you sit for longer than an hour, get up every 50 minutes and walk or stretch for 10 minutes.
- For heavy objects, bend your knees, attach them to your body, tighten your abdomen, and lift them without bending your waist.
- Stretch and back pain prevention exercises that do not strain your spine.
BlackGreenCo helps you build a healthy body through these three methods:
The fascia relaxation, steady stretching, and muscle strengthening through proper exercise
If you are interested or have any questions about this class,
Please contact blackgreenco@gmail.com
'Pain & Disease' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spondylolistesis (0) | 2020.06.01 |
|---|---|
| Spinal stenosis (4) | 2020.05.28 |
| Back pain (1) | 2020.05.25 |
| Asymmetric pelvic (2) | 2020.05.15 |
| Scoliosis (0) | 2020.05.07 |



